What Muscles Does a Recumbent Bike Work?
A recumbent bike is a great piece of gym equipment that offers accessible cardio workouts. But, along with fat-burning, the best recumbent exercise bikes provide a pretty good lower body workout.
So, on that note, let’s look at what muscles a recumbent bike works and answer the common question on what does a recumbent bike tone.
What is a Recumbent Bike?
A recumbent bike is an exercise machine that allows you to peddle while sitting in a recumbent (reclined) position. It is called a recumbent bike due to the nature of the seated position.
Among other things, this makes it more accessible for reaching the pedals and more comfortable because you typically get to sit on a normal seat rather than a bike seat.
The sitting position makes them suitable for gym novices and experts alike. They can be a good transitional machine but offer plenty of flexibility in workout routines.

Muscles Used Recumbent Bike vs. Upright Bike
We won’t get too deep into the differences between recumbent and upright bikes, as that’s not the point of this article. However, it’s worth highlighting some of the bigger differences because they can relate to the muscle groups worked.
Both bikes provide lower body workouts. Recumbent bikes provide more upper body support while doing so, as you sit on a chair with a back. This helps to reduce muscle fatigue and burn fat, meaning you can stick with the workout for longer.
By extension, upright bikes provide more of a full body workout, whereas recumbent bikes focus on the lower body. This should be enough information for you to decide which is right for your needs.
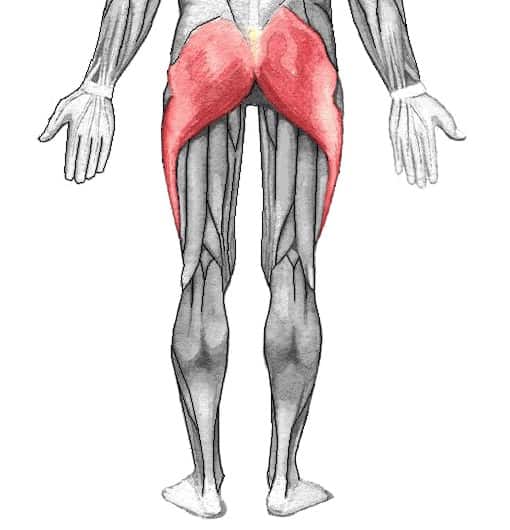
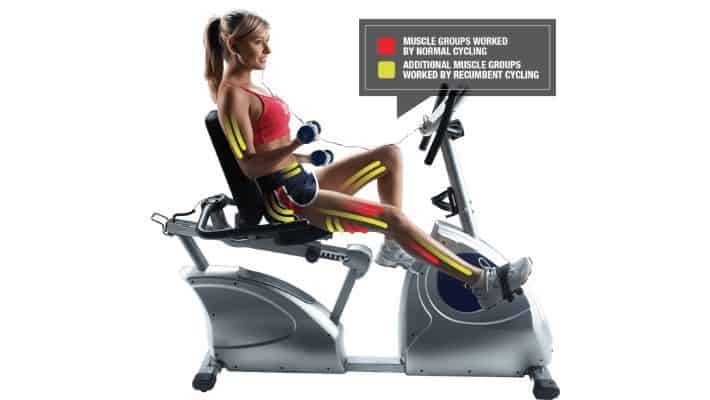
What Muscles do Recumbent Bikes Work?
So, we know that recumbent bikes work the lower body, but let’s look at that in more detail.
Does a recumbent bike work your thighs?
Glutes and Quads
Your gluteus muscles make up your bum and are instrumental in leg extension. You use your glutes every time you push down on a pedal.
As the opposite of this movement, your quads help draw the pedal back up along with aiding your glutes in pushing it down. The quads consist of 4 muscles:
- Rectus femoris
- Vastus intermedius
- Vastus medialis
- Vastus lateralis
Pedalling also brings your adductor muscles into play, which are found in your inner thigh and promote good balance and support.
As you can see, a simple pedalling action is great for working almost all the muscles in your thighs, giving you a good return on investment for this action.
Better still, using a recumbent bike is a low-impact exercise, as your feet aren’t smashing into the ground every time you move. It gives your legs a chance to work out without the fear of impact-related injury.

Hamstrings
The hamstrings are the opposing muscle group of the quads. They’re in the back of the thigh, and their job is to flex the knee. Your hamstrings help pull the foot back to the top during the pedalling motion and also engage when your leg goes from straight to bent.
Although your hamstrings aren’t the primary muscle group engaged when cycling, it can be a good form of exercise for strengthening them because it doesn’t put them under much pressure. You can use a recumbent bike for hamstring injury recovery or prevention.
Lower Legs
Your calves contain the meatier muscles in your lower legs, which are the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles. These help move your foot, including pointing your toes.
The shins contain the tibialis anterior muscles, the opposing group. They help pull your toes back from pointing.
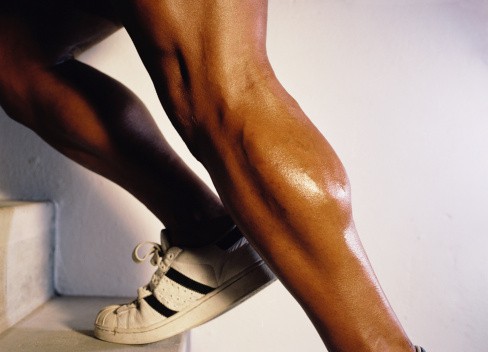
Cycling on a recumbent bike makes both muscle groups work hard. You rotate your feet as much as pump your legs, which helps exercise the front and back muscles of your lower legs.
For an extra tibialis anterior workout, use a recumbent bike with foot pedals. Doing so means you have more resistance when drawing your feet back up.
Does a Recumbent Bike Work Your Abs?
One unlikely body part you thought might be worked while using a recumbent bike is the abdominals. One of the primary purposes of the bucket seat on the machine is to engage your abdominal area during the workout.
You can even adjust the angle of the seat, to engage the abs more. This is because your abdominals are stabiliser muscles, which provide strength and balance throughout the whole body.

Arms
While recumbent bikes focus mainly on your lower body, some have arm cranks. Using these provides an upper body workout. But, if your machine doesn’t have cranks, you can theoretically add in any upper body workout you want.
Final Thoughts on Recumbent Bikes
Recumbent exercise bikes are good for lower body workouts if you want a comfortable and stable sitting position. While upright and spin bikes provide more of a full body workout, recumbent bikes are arguably more accessible.
Of course, if you want to get the most from your gym routine, you’ll switch between different machines anyway. If so, a recumbent bike is a great addition to a larger workout plan.
An ex-triathlete, fitness coach and writer with a Masters in Sports Physiology. Fitness is my passion and I've had my fair share of home fitness equipment tried and tested!


2 Comments